Communications Systems and Networks Lab (1.601A)
The Communications Systems and Networks lab offers equipment and practical experience in digital, wireless, and advanced communication systems, along with communication networks. The lab is designed to help students apply theoretical concepts in practice using a variety of communication devices.
Key Practical Experiments:
• Amplitude Modulation using Emona Tims and MATLAB
• Amplitude Demodulation using Emona Tims and MATLAB
• Frequency Modulation using Emona Tims and MATLAB
• Frequency Demodulation using Emona Tims and MATLAB
• Signal Sampling using Emona Tims
• Pulse Amplitude Modulation using Emona Tims
• Pulse Width Modulation using Emona Tims
• Pulse Position Modulation using Emona Tims
• Fundamentals of Designing Simple Local Area Networks (LANs)
• Physical Layer Protocols
• Characteristics of Transmission Media
• Data Link Layer Protocols
• Basic Switch Configuration
• Network Layer Protocols and IP Addressing
• Subnetting Configuration and Addressing
• Basics of Router Configuration
• Design of Simple and Complex Local Area Networks (LANs)
• Media Access Control Techniques
• Matched Filter Detection using EMONA TIMS
• Link Packet Analysis (Propagation Models, Path Loss Calculation, etc.)
• GSM Network: Coverage Predictions, Throughput Calculation, Traffic Analysis, and Network Dimensions
• TE Network: Coverage Predictions, Throughput Calculation, Traffic Analysis, and Network Dimensions
• Block Cipher Encryption and Decryption Implementation using EMONA TIMS
Key Equipment:
| photos | Equipment |
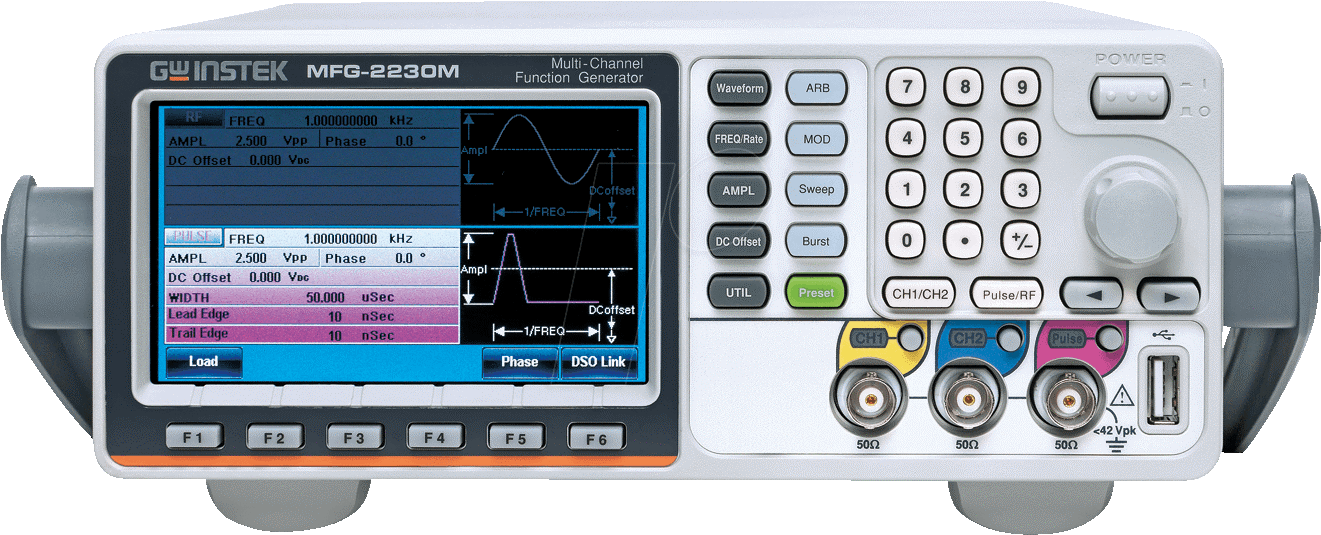
| wave form function generator |

| Telecommunications Instructional Modelling System - |
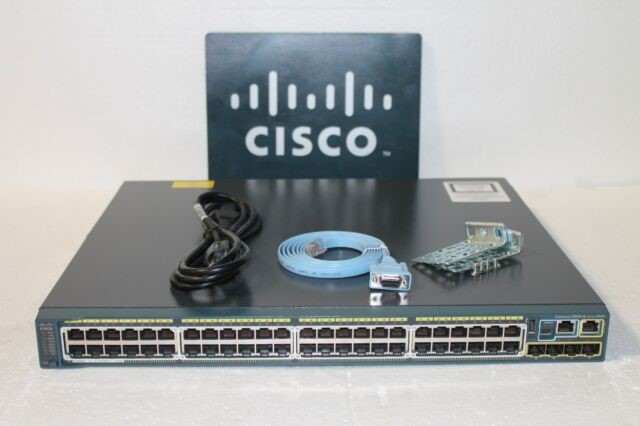

| wireless Access Point- |

| Router
|
Industrial Electronics, Solar Cells, and Nanotechnology Lab (1.601B)
The Industrial Electronics, Solar Cells, and Nanotechnology lab offers equipment and practical experience in industrial electronics, solar cells, and nanotechnology. The lab is designed to train students in research and development within industrial electronics, emphasizing manufacturing, measurement, and testing processes.
Key Practical Experiments:
• Demonstration of Solar Cell Manufacturing (First Generation)
• Demonstration of Solar Cell Manufacturing (Second Generation)
• Demonstration of Solar Cell Manufacturing (Third Generation)
• Solar Cell Characteristics: I-V Characteristics and Fill Factor
• Series and Parallel Connections of Photovoltaic Cells
• Optimal Incident Angle for a Solar Cell
• Solar Cell Efficiency
• Light Intensity and Light Filters
• Testing Loads on Photovoltaic Cells
• Output Current and Light Spectrum (Wavelength)
• Power Output and Temperature
• Scanning Tunneling Microscope (STM) - Basic Principle
• STM Scanning Functions
• Atomic Structure – High-Temperature Graphite (HOPG)
• Atomic Structure – Titanium, Tantalum, and Molybdenum Disulfide (MoS₂, TaS₂, TiS₂)
• Molecular Self-Assembly – Self-Assembled Monolayers (SAMs) on a Gold Surface
• Self-Assembly Systems – Monolayers of 60C Molecules
• Self-Assembly Systems – Carbon Nanotubes
Key Equipment:
equipment
| photos
|
Scanning tunne microscope (STM)
| 
|
Solar Energy Training System
| 
|
Antennas and Electromagnetic Waves Lab (1.601C)
The Antennas and Electromagnetic Waves lab offers equipment and practical experience in antennas and electromagnetic waves, supporting teaching, research, and development in the fields of electromagnetics and antenna technology. The lab specializes in the manufacturing, measurement, and testing of printed circuit boards, microwave circuits, antennas, and various radar systems.
Key Practical Experiments:
• Getting started with HFSS software – Waveguide T-Junction.
• Studying radiation of a λ/2 dipole antenna at 1 GHz.
• Designing a dipole antenna using HFSS.
• Studying radiation of an open waveguide at 10 GHz.
• Investigating the radiation properties of infinitesimal dipoles.
• Using MATLAB to solve Exercise 2.
• Measuring the gain of horn antennas.
• Exploring circular polarization and helical antennas.
• Understanding the equivalent antenna.
• Vectors and coordinate systems.
• Electrostatic fields.
• Applications of Vector Calculus.
• Gauss's Law and Electric Power.
• Dielectrics and Capacitance.
• Magnetic Fields.
• Oersted's Experiment.
• Ampère's Law.
• Magnetic Forces and Materials.
• Electromagnetic Induction.
• Applications of Boundary Conditions.
Key Equipment:

Photonic Electronics Lab (1.604B)
The lab provides equipment and practical experience that contribute to a deeper understanding of the principles of photonic electronics and optical communications.
Key Practical Experiments:
- Measuring light power
- Theoretical and practical verification of laser intensity
- Light polarization and focal length of thin lenses
- Determining the acceptance angle and numerical aperture of optical fibers
- Multi-mode graded-index fiber coupling
- Measuring fiber alignment loss
- Fiber splicing and introduction to OTDR (Optical Time Domain Reflectometer)
- Measuring fiber length and properties after splicing
- Characteristics of Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs)
- Characteristics of Photodiodes
Key Equipment:

Work Study Lab
This lab provides comprehensive knowledge about methods, measurements, and work management.
Key Practical Experiments:
- MOST (Maynard Operation Sequence Technique)
- Work Sample
Key Equipment:
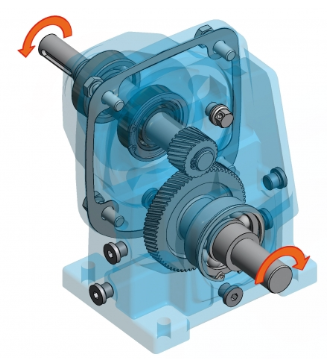
Spur gear Assembly Kit
| 
|
High-Speed Multi-Camera Motion Capture System
| 
|
Shut-off valve Assembly Kit
| 
|
Maintenance and Reliability Lab
This lab provides in-depth knowledge in the areas of machine diagnostics, calibration, and maintenance.
Key Practical Experiments:
- PT 500: Introduction to Machine Diagnostics System
- Single-Level Balancing
- Detection of Rotating Bearing Faults
- Effects of Gear Wear on Vibration Behavior
- Pressure Sensor Calibration
Key Equipment:
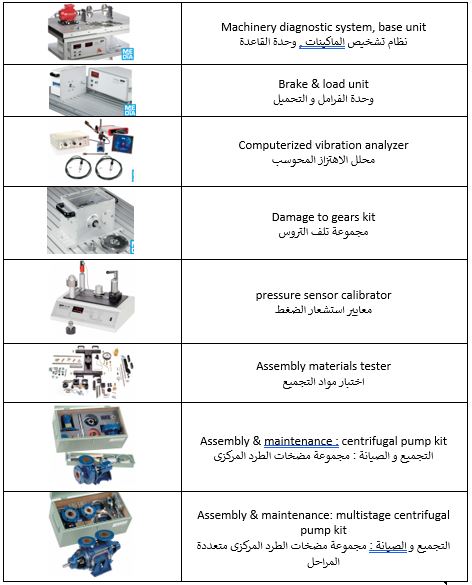
Measurement Lab:
This lab features a variety of measurement instruments that utilize precise techniques for measuring lengths, dimensions, and angles. It is also used for calibrating measuring devices and evaluating surface quality. Students engage in collecting and analyzing measurement data, assessing different methodologies, and understanding the strengths and limitations of various measurement techniques.
Key Practical Experiments:
- Measuring dimensions using a Vernier caliper
- Measuring dimensions with a micrometer and angle measuring device
- Measuring non-adjacent angles
- Measuring surface roughness
- Measuring linear and angular dimensions
- Product inspection using non-contact laser scanners
- Product inspection and testing using a touch probe
Key Equipment:
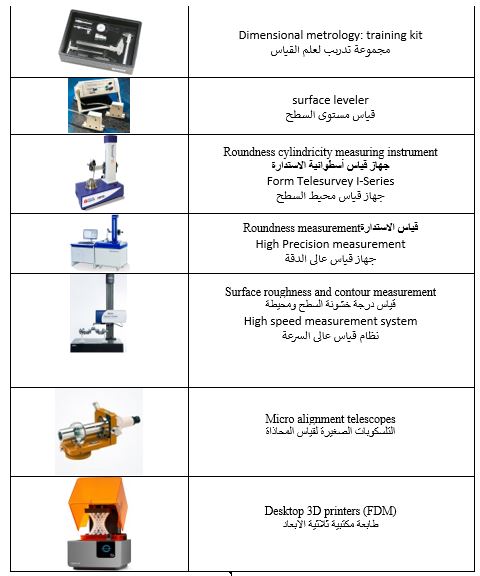
Materials Science and Engineering Lab
This lab offers in-depth knowledge of the properties, behaviors, and identification of manufacturing materials.
Key Practical Experiments:
- Hardness Testing
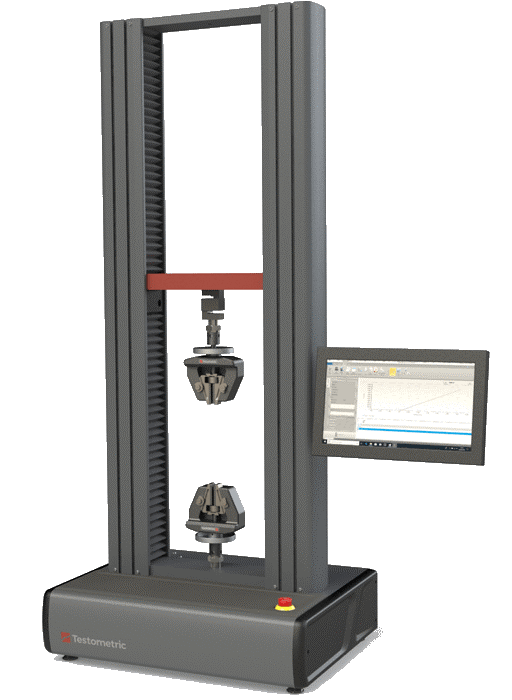
- Tensile Testing
- Charpy Impact Testing
- Torsion Testing
Key Equipment:
Charpy Testing Machine
|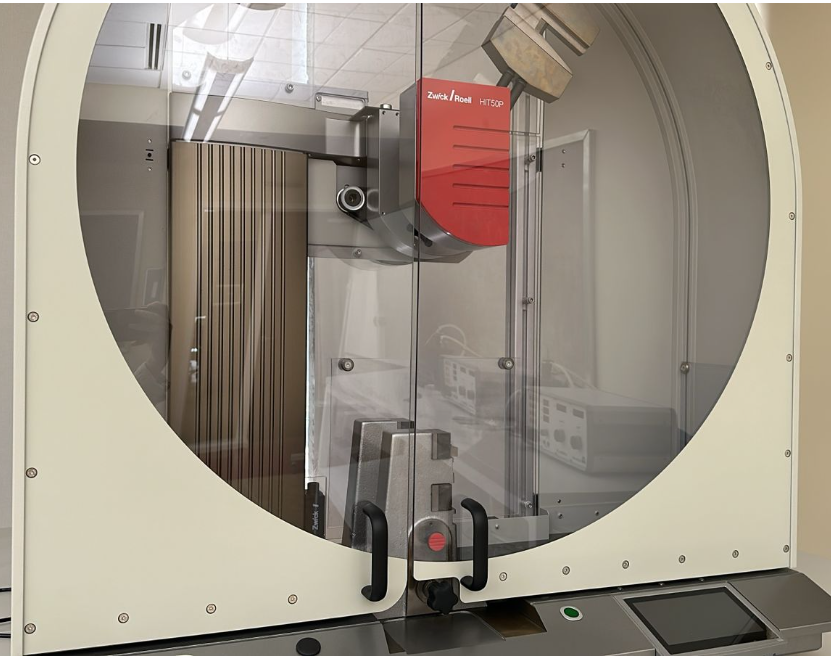  |
Optical microscope -Image capturing system
|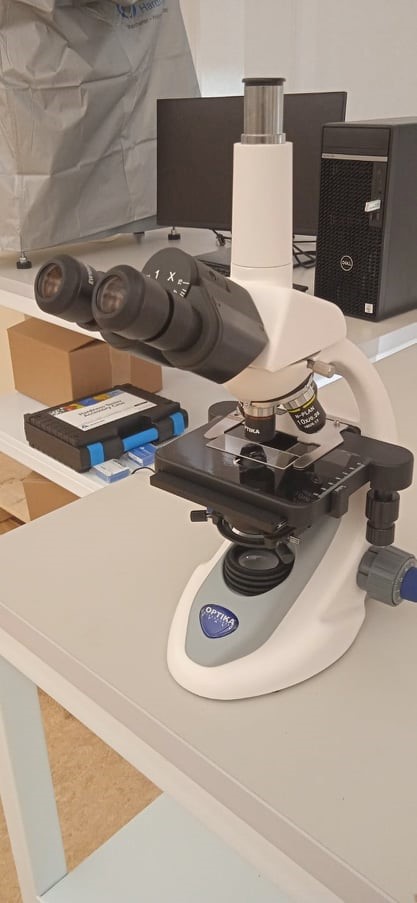  |
Brinell Hardness Testing Machine
|  |
Vickers Harness Testing Machine
|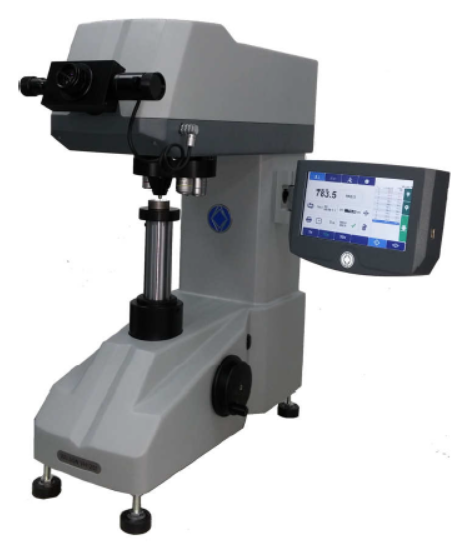  |
Rockwell Harness Testing Machine
| 
|
SFM- Test System
|  |
Torsion machine
|
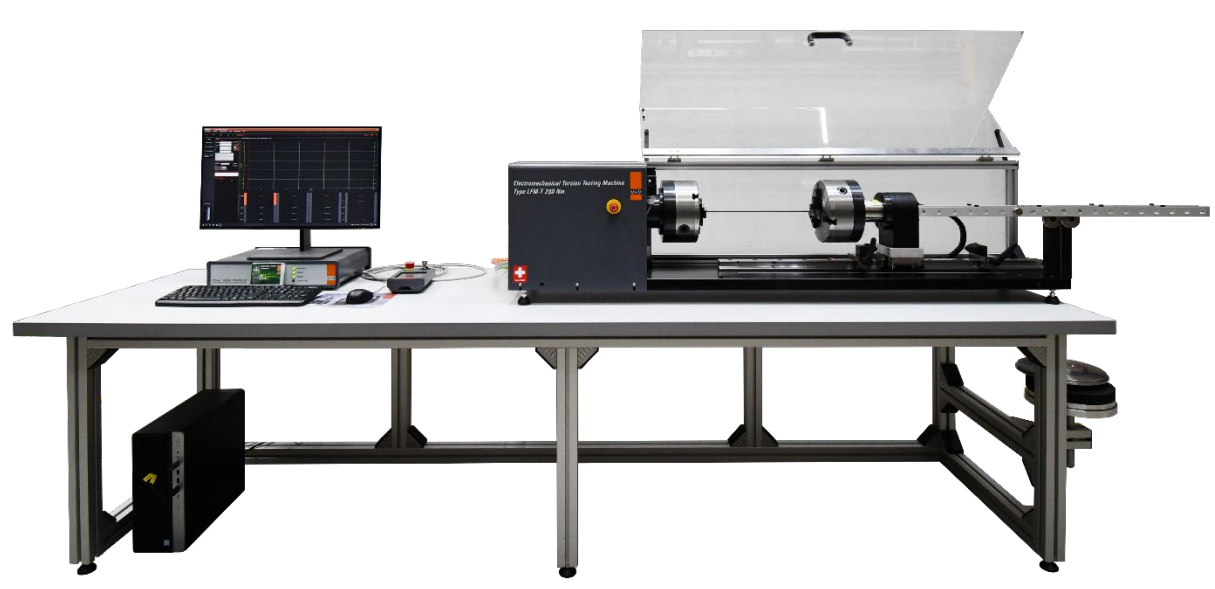

|
Human Factors Engineering Lab
This lab provides comprehensive knowledge of human factors principles.
Key Practical Experiments:
- Hearing Measurement
- Human Measurements and Work Design
- Light Intensity Measurement
- Measurement of Air Pollution and Gas Concentrations
- Measurement of Physical Workload
- Lifting Capacity Measurement
- Assessment of Poor Posture Using the RULA Method
- NIOSH Lifting Equation and Manual Material Handling
Engineering Drawing Lab
This lab provides comprehensive knowledge of engineering drawing, covering various aspects such as freehand drawing, dimensioning, tolerance determination, and the drawing of different types of lines through various projection theories.
Key Practical Experiments:
- Drawing standards, interference, and tolerance
- (Dimensioning, sectioning, title block) Introduction to 2D Drawing
- Special sections and curves
- Projections and sections
- Solid modeling of threads, basic shapes, and hierarchies
- Assembly drawing
- GUNT-based experimental sets
- Introduction to computer-aided drawing (CAD)
- Basic freehand drawing
Key Equipment:
| TZ-130 prismatic work samples with slanted cut-outs | 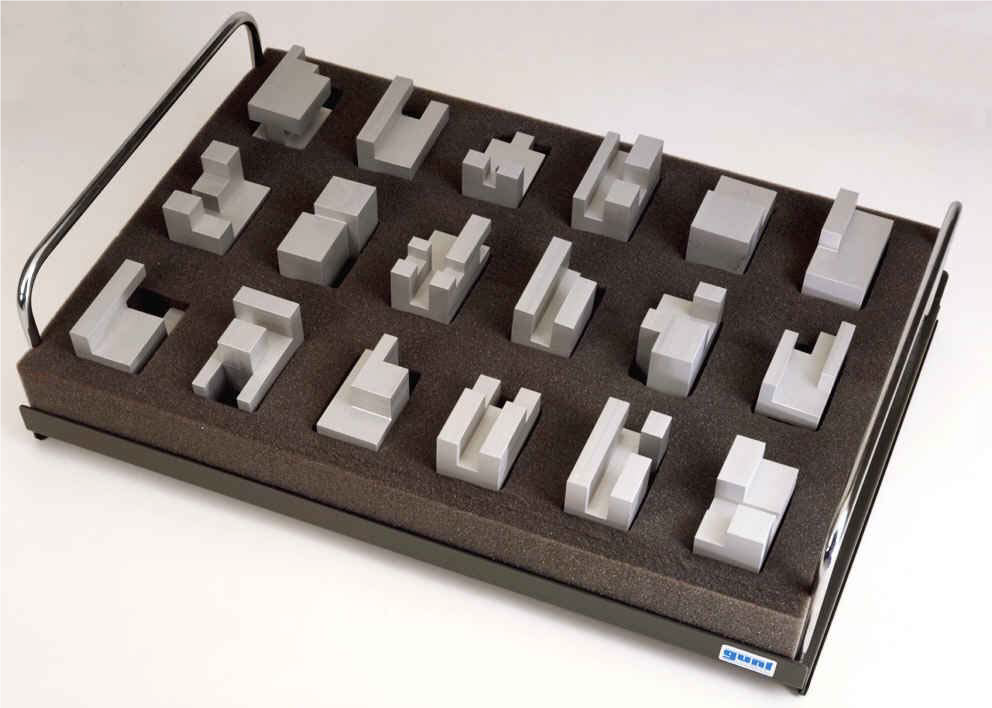
|
TZ-100 Engineering drawing three dimensional display |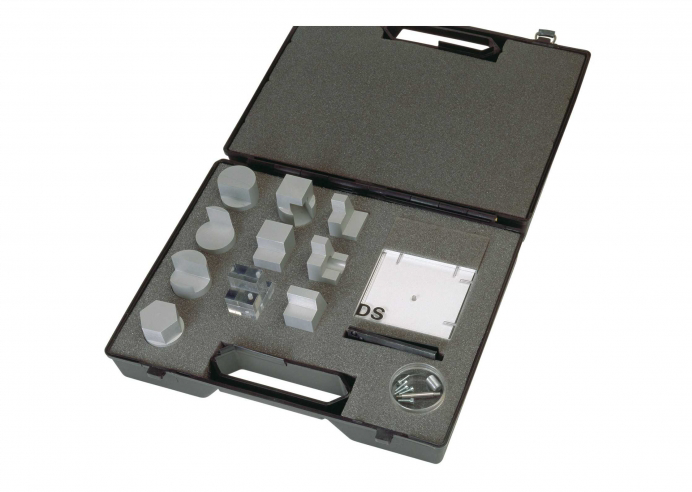  |
TZ 200.02 Engineering drawing casting | 
|
TZ 200.11 bending device : Assembly kit |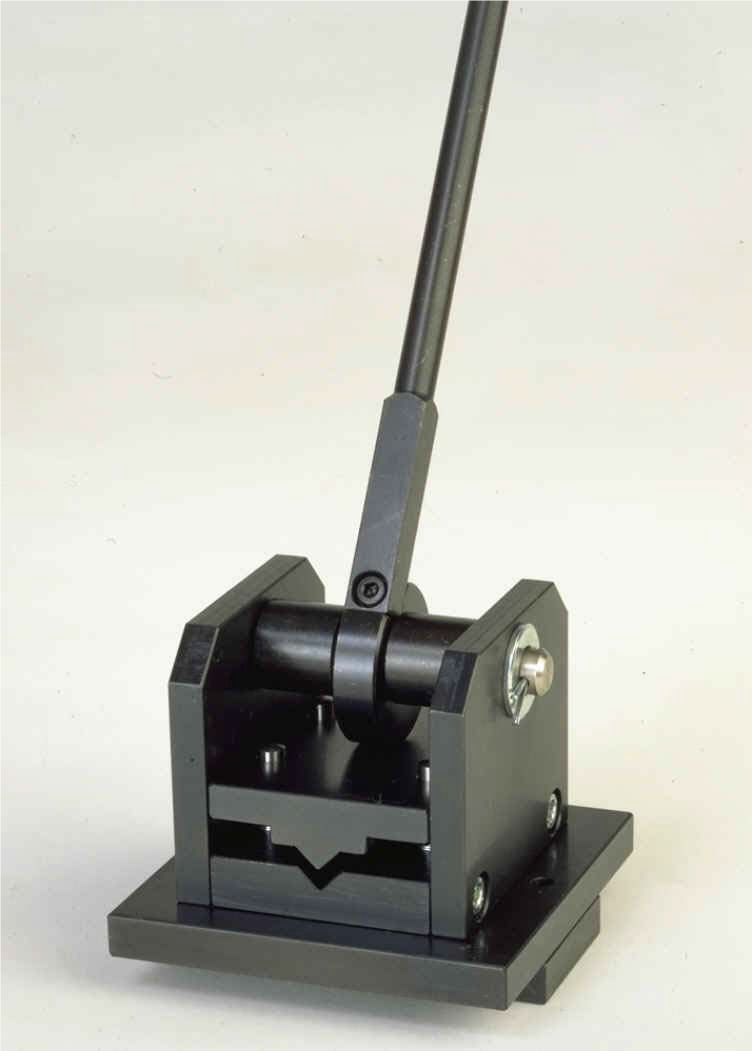  |
TZ 200.06: Drilling Jig for an annular disc | 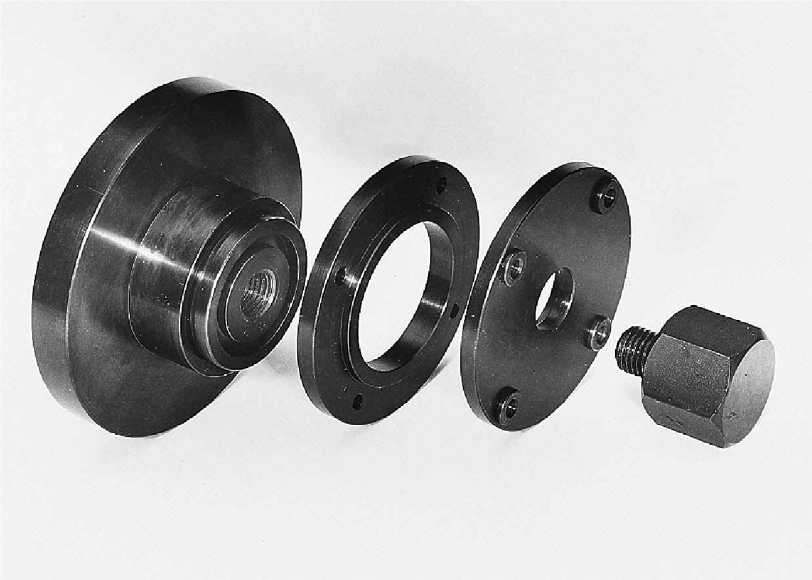
|